
![Learn the key terms in the biogas industry! Glossary of biogas, part 2/2 [M-Y]](https://biovoima.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Suomen-Biovoima_Biokaasu_sanasto_M-Y_header.jpg)
TS, VS, ymppi, mesophilic process, reject water... The language of biogas professionals is full of dozens of terms and abbreviations that may not be immediately clear to anyone interested. Discover the key terms and keep up to date with bioenergy terminology. Below is a list of terms and abbreviations in alphabetical order.
Biogas incineration at normal air pressure (around 1 bar) and a temperature of around +35°C.
Decomposition of organic matter by bacteria under anoxic conditions. The end product of the decomposition is biogas and a by-product of the process is the digestion residue, i.e. the treatment residue, which can be separated into dry and liquid fraction.
Treatment process for fractions with low dry matter content (DM < 15 %). In a biogas project, the long residence time of the wet process allows a higher fraction of the organic material in the feed to be degraded into biogas. It is a well established treatment process and often the optimal production process for slurry and sewage treatment plant sludge. In the wet process, for the reactor to function, the contents must be of very high homogeneity and more than 90 % of it must be water.
A normal cubic metre, i.e. a cubic metre of gas at normal pressure and 0°C. A unit of gas volume.
A long-term purchase agreement where the energy company, as the electricity user, agrees to buy a certain amount of electricity from the electricity producer at the contract price for a period of, say, 10-20 years. The power purchase agreement can be fixed or variable (e.g. based on exchange pricing). To make the biogas project profitable, CHP plant there must be a customer for electricity (and also heat) produced from biogas. In a biogas project, a power purchase agreement creates predictability and stability.
One of the techniques used in biogas processing that exploits the ability of gases to permeate a given material under pressure to distinguish between gases with different permeabilities. In other words, the adsorbent (typically activated carbon) binds the carbon dioxide in the raw gas at one pressure and releases it at another. The PSA process usually involves four or more columns in parallel. At least one column is in the adsorption phase, one in the desorption phase, and two are either depressurised or pressurised. The refined gas contains more than 97 % of methane.

In biogas, during the dry batching process, nutrient-rich water is released from the feed, which can be recycled back into the reactor as a nutrient. Percolation fluid recirculation ensures microbial circulation in the process, regulates the process moisture balance, degradation and gas production.
Gas treated for heating and electricity generation purposes by removing the generator from the and pollutants that cause harmful emissions. These pollutants are toxic to the CHP gas engine. Biomethane is often referred to as purified gas.
Gas from a source such as a landfill or natural gas well. Raw gas is often cleaned or refined in a gas treatment plant before further use and recovery.
Nitrogen- and potassium-containing liquid fraction separated from the treatment residue during separation. The reject water can be used as a soil improver or fertiliser if the raw materials in the plant are of plant and animal origin. Reject water can also be recycled from the downstream end of the reactor to the upstream end, acting as a nutrient.
Organic material to be treated in a biogas plant. The biogas plant is fed with including household biowaste bags, contaminated food, crop residues, animal manure, slaughterhouse waste and sludge from sewage treatment plants. If the microbes in a biogas plant are not fed, biogas production will be stagnant.
A mixture of different inputs, mixed in appropriate proportions, which is processed in a biogas plant. In many cases, an effective feed mixture can produce a more balanced ammonia and nitrogen feed with added value for further use, e.g. it can contribute to the possibility of using the treatment residue as fertiliser.
Biogas incineration at normal air pressure (about 1 bar) and a temperature of about +55°C.
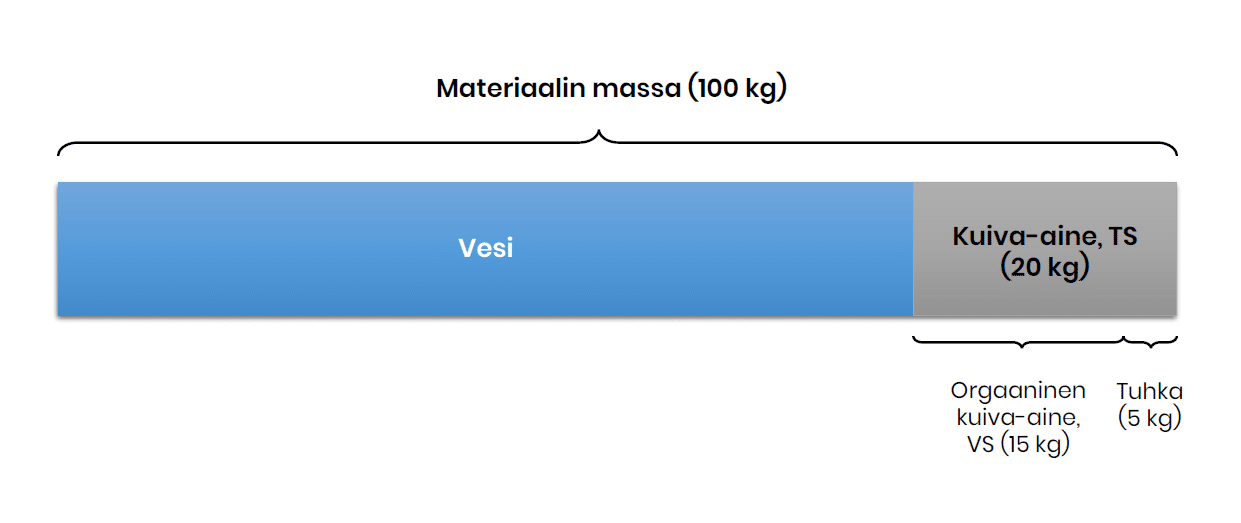
The dry matter content of the feed after removal of the liquid, including both inorganic (i.e. ash) and organic matter. Also abbreviated DM (dry matter). One of the most important quality characteristics of the feed. Expressed as a percentage.
The proportion of organic matter in the dried matter (i.e. DM). Also abbreviated as oDM (organic dry matter). One of the most important quality characteristics of the feed. Expressed as a percentage.
A reusable bacterial culture, for example a treatment residue from a functioning biogas reactor, intended to maintain a microbial population in another biogas plant. Can serve as an initial step in the upgrading of a new reactor.
Environmental impact assessment procedure. An EIA aims to reduce or eliminate the adverse environmental impacts of a project. An EIA procedure is required for treatment volumes above 35 000 t/a or for projects likely to have significant environmental impacts. If an EIA procedure is required, the authority cannot grant an environmental permit for a new biogas plant without an EIA report and an opinion from the contact authority.



"*" näyttää pakolliset kentät

© 2026 Biovoima
Privacy policy
